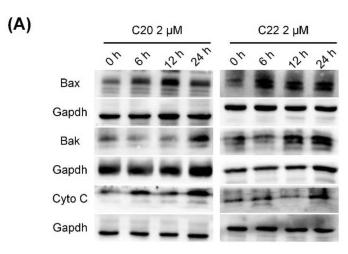
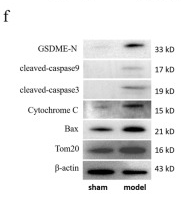
Cytochrome C Antibody - #AF0146
| Product: | Cytochrome C Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0146 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Cytochrome C |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 15kDa; 12kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P99999 |
| RRID: | AB_2833328 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0146, RRID:AB_2833328.
Fold/Unfold
CYC; CYC_HUMAN; CYCS; Cytochrome c; Cytochrome c somatic; HCS; THC4;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Cytochrome C, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
- P99999 CYC_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGDVEKGKKIFIMKCSQCHTVEKGGKHKTGPNLHGLFGRKTGQAPGYSYTAANKNKGIIWGEDTLMEYLENPKKYIPGTKMIFVGIKKKEERADLIAYLKKATNE
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Electron carrier protein. The oxidized form of the cytochrome c heme group can accept an electron from the heme group of the cytochrome c1 subunit of cytochrome reductase. Cytochrome c then transfers this electron to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the final protein carrier in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain.
Plays a role in apoptosis. Suppression of the anti-apoptotic members or activation of the pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family leads to altered mitochondrial membrane permeability resulting in release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. Binding of cytochrome c to Apaf-1 triggers the activation of caspase-9, which then accelerates apoptosis by activating other caspases.
Binds 1 heme group per subunit.
Phosphorylation at Tyr-49 and Tyr-98 both reduce by half the turnover in the reaction with cytochrome c oxidase, down-regulating mitochondrial respiration.
Mitochondrion intermembrane space.
Note: Loosely associated with the inner membrane.
Belongs to the cytochrome c family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Platinum drug resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Parkinson's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Huntington's disease.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Viral myocarditis.
· Metabolism > Energy metabolism > Sulfur metabolism.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
References
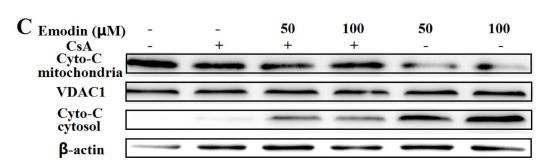
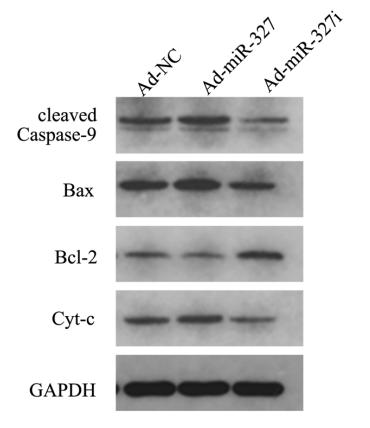
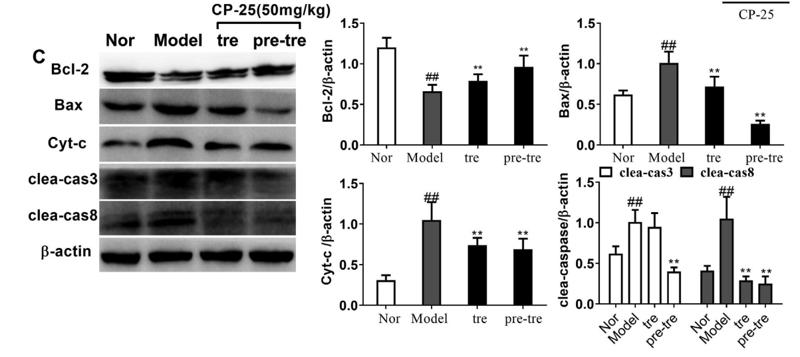
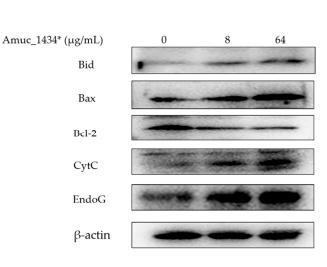
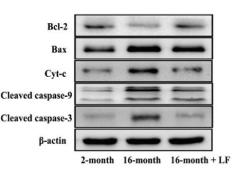
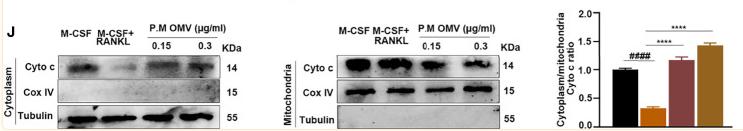
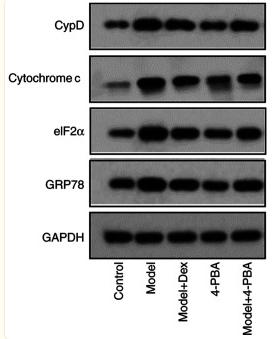
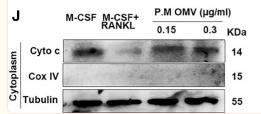
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: B cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HUVECs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.