CREB-BP Antibody - #AF0139
| Product: | CREB-BP Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0139 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CREB-BP |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 265kDa; 265kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q92793 |
| RRID: | AB_2833321 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0139, RRID:AB_2833321.
Fold/Unfold
CBP; CBP_HUMAN; CREB binding protein; CREB-binding protein; Crebbp; Cyclic AMP responsive enhancer binding protein; KAT3A; RSTS; RTS; Rubinstein Taybi syndrome;
Immunogens
- Q92793 CBP_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAENLLDGPPNPKRAKLSSPGFSANDSTDFGSLFDLENDLPDELIPNGGELGLLNSGNLVPDAASKHKQLSELLRGGSGSSINPGIGNVSASSPVQQGLGGQAQGQPNSANMASLSAMGKSPLSQGDSSAPSLPKQAASTSGPTPAASQALNPQAQKQVGLATSSPATSQTGPGICMNANFNQTHPGLLNSNSGHSLINQASQGQAQVMNGSLGAAGRGRGAGMPYPTPAMQGASSSVLAETLTQVSPQMTGHAGLNTAQAGGMAKMGITGNTSPFGQPFSQAGGQPMGATGVNPQLASKQSMVNSLPTFPTDIKNTSVTNVPNMSQMQTSVGIVPTQAIATGPTADPEKRKLIQQQLVLLLHAHKCQRREQANGEVRACSLPHCRTMKNVLNHMTHCQAGKACQVAHCASSRQIISHWKNCTRHDCPVCLPLKNASDKRNQQTILGSPASGIQNTIGSVGTGQQNATSLSNPNPIDPSSMQRAYAALGLPYMNQPQTQLQPQVPGQQPAQPQTHQQMRTLNPLGNNPMNIPAGGITTDQQPPNLISESALPTSLGATNPLMNDGSNSGNIGTLSTIPTAAPPSSTGVRKGWHEHVTQDLRSHLVHKLVQAIFPTPDPAALKDRRMENLVAYAKKVEGDMYESANSRDEYYHLLAEKIYKIQKELEEKRRSRLHKQGILGNQPALPAPGAQPPVIPQAQPVRPPNGPLSLPVNRMQVSQGMNSFNPMSLGNVQLPQAPMGPRAASPMNHSVQMNSMGSVPGMAISPSRMPQPPNMMGAHTNNMMAQAPAQSQFLPQNQFPSSSGAMSVGMGQPPAQTGVSQGQVPGAALPNPLNMLGPQASQLPCPPVTQSPLHPTPPPASTAAGMPSLQHTTPPGMTPPQPAAPTQPSTPVSSSGQTPTPTPGSVPSATQTQSTPTVQAAAQAQVTPQPQTPVQPPSVATPQSSQQQPTPVHAQPPGTPLSQAAASIDNRVPTPSSVASAETNSQQPGPDVPVLEMKTETQAEDTEPDPGESKGEPRSEMMEEDLQGASQVKEETDIAEQKSEPMEVDEKKPEVKVEVKEEEESSSNGTASQSTSPSQPRKKIFKPEELRQALMPTLEALYRQDPESLPFRQPVDPQLLGIPDYFDIVKNPMDLSTIKRKLDTGQYQEPWQYVDDVWLMFNNAWLYNRKTSRVYKFCSKLAEVFEQEIDPVMQSLGYCCGRKYEFSPQTLCCYGKQLCTIPRDAAYYSYQNRYHFCEKCFTEIQGENVTLGDDPSQPQTTISKDQFEKKKNDTLDPEPFVDCKECGRKMHQICVLHYDIIWPSGFVCDNCLKKTGRPRKENKFSAKRLQTTRLGNHLEDRVNKFLRRQNHPEAGEVFVRVVASSDKTVEVKPGMKSRFVDSGEMSESFPYRTKALFAFEEIDGVDVCFFGMHVQEYGSDCPPPNTRRVYISYLDSIHFFRPRCLRTAVYHEILIGYLEYVKKLGYVTGHIWACPPSEGDDYIFHCHPPDQKIPKPKRLQEWYKKMLDKAFAERIIHDYKDIFKQATEDRLTSAKELPYFEGDFWPNVLEESIKELEQEEEERKKEESTAASETTEGSQGDSKNAKKKNNKKTNKNKSSISRANKKKPSMPNVSNDLSQKLYATMEKHKEVFFVIHLHAGPVINTLPPIVDPDPLLSCDLMDGRDAFLTLARDKHWEFSSLRRSKWSTLCMLVELHTQGQDRFVYTCNECKHHVETRWHCTVCEDYDLCINCYNTKSHAHKMVKWGLGLDDEGSSQGEPQSKSPQESRRLSIQRCIQSLVHACQCRNANCSLPSCQKMKRVVQHTKGCKRKTNGGCPVCKQLIALCCYHAKHCQENKCPVPFCLNIKHKLRQQQIQHRLQQAQLMRRRMATMNTRNVPQQSLPSPTSAPPGTPTQQPSTPQTPQPPAQPQPSPVSMSPAGFPSVARTQPPTTVSTGKPTSQVPAPPPPAQPPPAAVEAARQIEREAQQQQHLYRVNINNSMPPGRTGMGTPGSQMAPVSLNVPRPNQVSGPVMPSMPPGQWQQAPLPQQQPMPGLPRPVISMQAQAAVAGPRMPSVQPPRSISPSALQDLLRTLKSPSSPQQQQQVLNILKSNPQLMAAFIKQRTAKYVANQPGMQPQPGLQSQPGMQPQPGMHQQPSLQNLNAMQAGVPRPGVPPQQQAMGGLNPQGQALNIMNPGHNPNMASMNPQYREMLRRQLLQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQGSAGMAGGMAGHGQFQQPQGPGGYPPAMQQQQRMQQHLPLQGSSMGQMAAQMGQLGQMGQPGLGADSTPNIQQALQQRILQQQQMKQQIGSPGQPNPMSPQQHMLSGQPQASHLPGQQIATSLSNQVRSPAPVQSPRPQSQPPHSSPSPRIQPQPSPHHVSPQTGSPHPGLAVTMASSIDQGHLGNPEQSAMLPQLNTPSRSALSSELSLVGDTTGDTLEKFVEGL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q92793 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K13 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S78 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S92 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S93 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) , P27361 (MAPK3) | Uniprot |
| S121 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S124 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S129 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R220 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S274 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S302 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T320 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K366 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K389 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S437 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R601 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K622 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K657 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| Y659 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R714 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| R742 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| R768 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| T1001 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1014 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S1019 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1030 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1033 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K1042 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S1043 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1056 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| T1070 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1072 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1076 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y1125 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1171 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1203 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1216 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| R1341 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K1367 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1376 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S1382 | Phosphorylation | O15111 (CHUK) | Uniprot |
| S1386 | Phosphorylation | O15111 (CHUK) | Uniprot |
| Y1391 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1524 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1535 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1535 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K1564 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1565 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S1568 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1569 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1578 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1583 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1586 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1587 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1588 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1591 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1592 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1595 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1597 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1620 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| Y1622 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1627 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| T1669 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1697 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1711 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1736 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1741 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1744 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S1754 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1755 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1762 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S1763 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1791 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1797 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1799 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1806 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1809 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1831 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K1837 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| T1871 | Phosphorylation | P31749 (AKT1) | Uniprot |
| T1874 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1937 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| Y1973 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2041 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2063 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2065 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T2073 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K2075 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S2076 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2078 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2079 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K2102 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S2351 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R2353 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S2356 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2361 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2362 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2364 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2406 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2422 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S2425 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Acetylates histones, giving a specific tag for transcriptional activation. Also acetylates non-histone proteins, like DDX21, FBL, IRF2, MAFG, NCOA3, POLR1E/PAF53 and FOXO1. Binds specifically to phosphorylated CREB and enhances its transcriptional activity toward cAMP-responsive genes. Acts as a coactivator of ALX1. Acts as a circadian transcriptional coactivator which enhances the activity of the circadian transcriptional activators: NPAS2-ARNTL/BMAL1 and CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimers. Acetylates PCNA; acetylation promotes removal of chromatin-bound PCNA and its degradation during nucleotide excision repair (NER). Acetylates POLR1E/PAF53, leading to decreased association of RNA polymerase I with the rDNA promoter region and coding region. Acetylates DDX21, thereby inhibiting DDX21 helicase activity. Acetylates FBL, preventing methylation of 'Gln-105' of histone H2A (H2AQ104me). Functions as a transcriptional coactivator for SMAD4 in the TGF-beta signaling pathway.
Methylation of the KIX domain by CARM1 blocks association with CREB. This results in the blockade of CREB signaling, and in activation of apoptotic response (By similarity).
Phosphorylated by CHUK/IKKA at Ser-1382 and Ser-1386; these phosphorylations promote cell growth by switching the binding preference of CREBBP from TP53 to NF-kappa-B.
Sumoylation negatively regulates transcriptional activity via the recruitment of DAAX.
Autoacetylation is required for binding to protein substrates, such as acetylated histones and acetylated TP53/p53.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Recruited to nuclear bodies by SS18L1/CREST. In the presence of ALX1 relocalizes from the cytoplasm to the nucleus.
Found in a complex containing NCOA2; NCOA3; IKKA; IKKB and IKBKG. Probably part of a complex with HIF1A and EP300. Interacts with GATA1; the interaction results in acetylation and enhancement of transcriptional activity of GATA1. Interacts with MAF AND ZCCHC12. Interacts with DAXX; the interaction is dependent on CBP sumoylation and results in suppression of the transcriptional activity via recruitment of HDAC2 to DAXX (By similarity). Interacts with phosphorylated CREB1. Interacts with CITED4 (C-terminal region). Interacts (via the TAZ-type 1 domain) with HIF1A. Interacts with SRCAP, CARM1, ELF3, MLLT7/FOXO4, N4BP2, NCOA1, NCOA3, NCOA6, PCAF, DDX5, DDX17, PELP1, PML, SMAD1, SMAD2, SMAD3, SPIB and TRERF1. Interacts with KLF1; the interaction results in acetylation of KLF1 and enhancement of its transcriptional activity. Interacts with MTDH. Interacts with NFATC4. Interacts with MAFG; the interaction acetylates MAFG in the basic region and stimulates NFE2 transcriptional activity through increasing its DNA-binding activity. Interacts with IRF2; the interaction acetylates IRF2 and regulates its activity on the H4 promoter. Interacts with IRF3 (when phosphorylated); forming the dsRNA-activated factor 1 (DRAF1), a complex which activates the transcription of the type I interferon genes. Interacts (via N-terminus) with SS18L1/CREST (via C-terminus). Interacts with MECOM. Interacts with CITED1 (via C-terminus). Interacts with FOXO1; the interaction acetylates FOXO1 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Interacts with NPAS2, CLOCK and ARNTL/BMAL1. Interacts with ASF1A and ASF1B; this promotes histone acetylation. Interacts with acetylated TP53/p53 and with the acetylated histones H3 and H4. Interacts (via transactivation domain and C-terminus) with PCNA; the interaction occurs on chromatin in UV-irradiated damaged cells. Interacts with DHX9 (via N-terminus); this interaction mediates association with RNA polymerase II holoenzyme and stimulates CREB-dependent transcriptional activation. Interacts with SMAD4; negatively regulated by ZBTB7A. Interacts with DUX4 (via C-terminus). Forms a complex with KMT2A and CREB1. Interacts with DDX3X; this interaction may facilitate HNF4A acetylation.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HTLV-1 Tax, p30II and HBZ.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with human herpes virus 8/HHV-8 protein vIRF-1; this interaction inhibits CREBBP binding to IRF3.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 Tat.
The KIX domain mediates binding to HIV-1 Tat.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Notch signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Huntington's disease.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
References
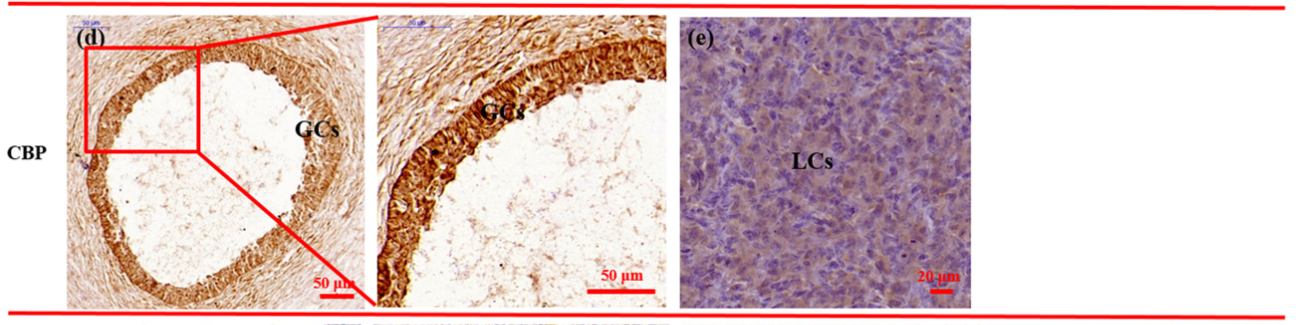
Application: IHC Species: Hu sheep Sample: GCs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.