NQO1 Antibody - #DF6437
| Product: | NQO1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6437 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to NQO1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 31kDa; 31kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P15559 |
| RRID: | AB_2838400 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6437, RRID:AB_2838400.
Fold/Unfold
Azoreductase; Cytochrome b 5 reductase; DHQU; DIA 4; DIA4; Diaphorase (NADH/NADPH) (cytochrome b 5 reductase); Diaphorase (NADH/NADPH); Diaphorase 4; Dioxin inducible 1; DT diaphorase; DT-diaphorase; DTD; Menadione reductase; NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1; NAD(P)H dehydrogenase quinone 1; NAD(P)H menadione oxidoreductase 1 dioxin inducible; NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1; NAD(P)H: menadione oxidoreductase 1 dioxin inducible 1; NAD(P)H:menadione oxidoreductase 1; NAD(P)H:Quinone acceptor oxidoreductase type 1; NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1; NAD(P)H:quinone oxireductase; NMOR 1; NMOR I; NMOR1; NMORI; NQO 1; NQO1; NQO1_HUMAN; Phylloquinone reductase; QR 1; QR1; Quinone reductase 1;
Immunogens
- P15559 NQO1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MVGRRALIVLAHSERTSFNYAMKEAAAAALKKKGWEVVESDLYAMNFNPIISRKDITGKLKDPANFQYPAESVLAYKEGHLSPDIVAEQKKLEAADLVIFQFPLQWFGVPAILKGWFERVFIGEFAYTYAAMYDKGPFRSKKAVLSITTGGSGSMYSLQGIHGDMNVILWPIQSGILHFCGFQVLEPQLTYSIGHTPADARIQILEGWKKRLENIWDETPLYFAPSSLFDLNFQAGFLMKKEVQDEEKNKKFGLSVGHHLGKSIPTDNQIKARK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - P15559 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| S13 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y20 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K23 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K31 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K31 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K33 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S40 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y43 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K54 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K59 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K59 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K61 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y68 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y76 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K77 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K77 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S82 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K90 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K91 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y127 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y129 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y133 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K135 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K209 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K209 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K210 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K210 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K241 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K248 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K251 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K251 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S255 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K262 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K262 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K271 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K271 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
The enzyme apparently serves as a quinone reductase in connection with conjugation reactions of hydroquinons involved in detoxification pathways as well as in biosynthetic processes such as the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation of glutamate residues in prothrombin synthesis.
Cytoplasm.
Homodimer. Interacts with PDLIM4 isoform 2; this interaction stabilizes PDLIM4 isoform 2 in response to oxidative stress and protects it from ubiquitin-independent degradation by the core 20S proteasome.
Belongs to the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Metabolism > Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins > Ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis.
References
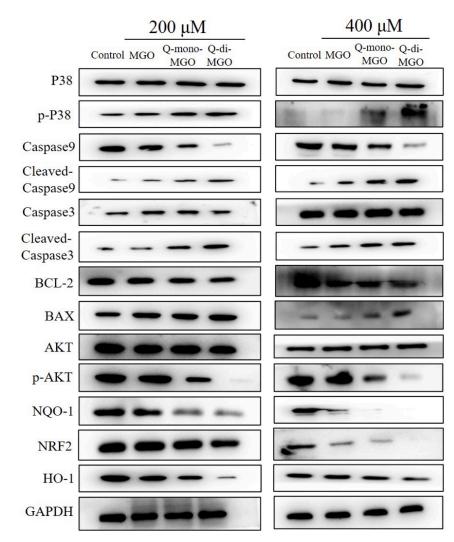
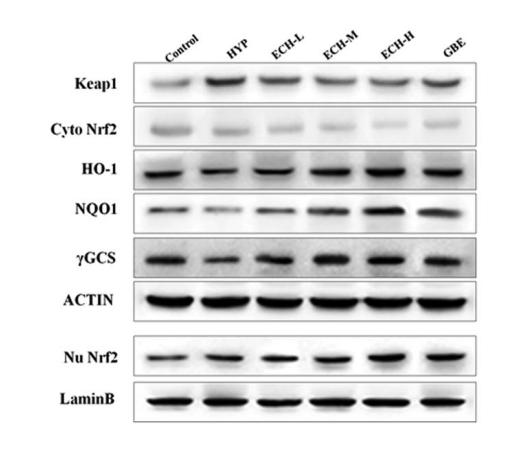
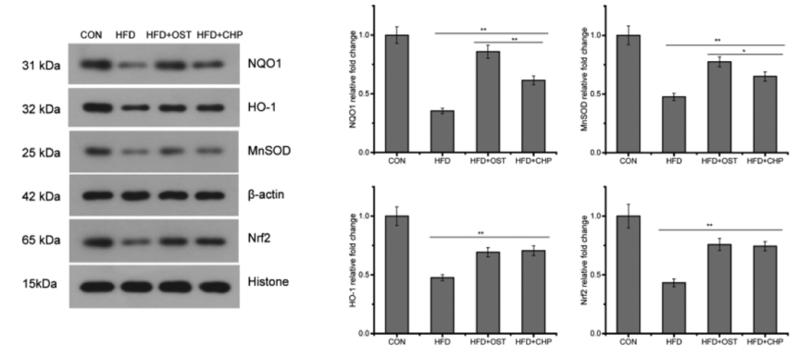
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: PC-12 cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: PC12 cells
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: kidney
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: Hippocampi
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: white adipose
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: kidney
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.