Smad4 Antibody - #AF5247
| Product: | Smad4 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5247 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Smad4 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 65 kDa; 60kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q13485 |
| RRID: | AB_2837733 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5247, RRID:AB_2837733.
Fold/Unfold
(Small) Mothers Against Decapentaplegic; Deleted in Pancreatic Carcinoma 4; Deleted in Pancreatic Carcinoma; Deleted in pancreatic carcinoma locus 4; Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4; DPC 4; DPC4; hSMAD4; JIP; MAD homolog 4; MAD mothers against decapentaplegic Drosophila homolog 4; MAD mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4; MADH 4; MADH4; Med; Medea; Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4; Mothers against decapentaplegic, Drosophila, homolog of, 4; Mothers against DPP homolog 4; MYHRS; OTTHUMP00000163548; SMA- and MAD-related protein 4; SMAD 4; SMAD family member 4; SMAD mothers against DPP homolog 4; SMAD4; SMAD4_HUMAN;
Immunogens
- Q13485 SMAD4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDNMSITNTPTSNDACLSIVHSLMCHRQGGESETFAKRAIESLVKKLKEKKDELDSLITAITTNGAHPSKCVTIQRTLDGRLQVAGRKGFPHVIYARLWRWPDLHKNELKHVKYCQYAFDLKCDSVCVNPYHYERVVSPGIDLSGLTLQSNAPSSMMVKDEYVHDFEGQPSLSTEGHSIQTIQHPPSNRASTETYSTPALLAPSESNATSTANFPNIPVASTSQPASILGGSHSEGLLQIASGPQPGQQQNGFTGQPATYHHNSTTTWTGSRTAPYTPNLPHHQNGHLQHHPPMPPHPGHYWPVHNELAFQPPISNHPAPEYWCSIAYFEMDVQVGETFKVPSSCPIVTVDGYVDPSGGDRFCLGQLSNVHRTEAIERARLHIGKGVQLECKGEGDVWVRCLSDHAVFVQSYYLDREAGRAPGDAVHKIYPSAYIKVFDLRQCHRQMQQQAATAQAAAAAQAAAVAGNIPGPGSVGGIAPAISLSAAAGIGVDDLRRLCILRMSFVKGWGPDYPRQSIKETPCWIEIHLHRALQLLDEVLHTMPIADPQPLD
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q13485 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| T9 | Phosphorylation | Q9UBE8 (NLK) | Uniprot |
| S22 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S32 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K37 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K45 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K45 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K48 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K70 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T77 | Phosphorylation | Q15831 (STK11) | Uniprot |
| Y95 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K106 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K113 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K113 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K122 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S138 | Phosphorylation | Q9UBE8 (NLK) | Uniprot |
| K159 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| S178 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T265 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T269 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T273 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T277 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) , P27361 (MAPK3) | Uniprot |
| S343 | Phosphorylation | Q14680 (MELK) | Uniprot |
| K385 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K428 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S504 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K507 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K507 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y513 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K519 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
In muscle physiology, plays a central role in the balance between atrophy and hypertrophy. When recruited by MSTN, promotes atrophy response via phosphorylated SMAD2/4. MSTN decrease causes SMAD4 release and subsequent recruitment by the BMP pathway to promote hypertrophy via phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8. Acts synergistically with SMAD1 and YY1 in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-mediated cardiac-specific gene expression. Binds to SMAD binding elements (SBEs) (5'-GTCT/AGAC-3') within BMP response element (BMPRE) of cardiac activating regions (By similarity). Common SMAD (co-SMAD) is the coactivator and mediator of signal transduction by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor). Component of the heterotrimeric SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex that forms in the nucleus and is required for the TGF-mediated signaling. Promotes binding of the SMAD2/SMAD4/FAST-1 complex to DNA and provides an activation function required for SMAD1 or SMAD2 to stimulate transcription. Component of the multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex which forms at the AP1 promoter site; required for synergistic transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta. May act as a tumor suppressor. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator.
Phosphorylated by PDPK1.
Monoubiquitinated on Lys-519 by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33. Monoubiquitination hampers its ability to form a stable complex with activated SMAD2/3 resulting in inhibition of TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade. Deubiquitination by USP9X restores its competence to mediate TGF-beta signaling.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand. Migrates to the nucleus when complexed with R-SMAD (PubMed:15799969). PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236).
Found in a complex with SMAD1 and YY1 (By similarity). Interacts with CITED2 (By similarity). Monomer; in the absence of TGF-beta activation. Heterodimer; on TGF-beta activation. Composed of two molecules of a C-terminally phosphorylated R-SMAD molecule, SMAD2 or SMAD3, and one molecule of SMAD4 to form the transcriptional active SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex. Found in a ternary complex composed of SMAD4, STK11/LKB1 and STK11IP. Interacts with ATF2, COPS5, DACH1, MSG1, SKI, STK11/LKB1, STK11IP and TRIM33. Interacts with ZNF423; the interaction takes place in response to BMP2 leading to activation of transcription of BMP target genes. Interacts with ZNF521; the interaction takes place in response to BMP2 leading to activation of transcription of BMP target genes. Interacts with USP9X. Interacts (via the MH1 and MH2 domains) with RBPMS. Interacts with WWTR1 (via coiled-coil domain). Component of the multimeric complex SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS which forms at the AP1 promoter site; required for synergistic transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta. Interacts with CITED1. Interacts with PDPK1 (via PH domain) (By similarity). Interacts with VPS39; this interaction affects heterodimer formation with SMAD3, but not with SMAD2, and leads to inhibition of SMAD3-dependent transcription activation. Interactions with VPS39 and SMAD2 may be mutually exclusive. Interacts with ZC3H3 (By similarity). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with ZNF451 (via N-terminal zinc-finger domains). Identified in a complex that contains at least ZNF451, SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4. Interacts weakly with ZNF8. Interacts with NUP93 and IPO7; translocates SMAD4 to the nucleus through the NPC upon BMP7 stimulation resulting in activation of SMAD4 signaling. Interacts with CREB3L1, the interaction takes place upon TGFB1 induction and SMAD4 acts as CREB3L1 coactivator to induce the expression of genes involved in the assembly of collagen extracellular matrix. Interacts with DLX1. Interacts with ZBTB7A; the interaction is direct and stimulated by TGFB1. Interacts with CREBBP; the recruitment of this transcriptional coactivator is negatively regulated by ZBTB7A. Interacts with EP300; the interaction with this transcriptional coactivator is negatively regulated by ZBTB7A. Interacts with HDAC1. Interacts (via MH2 domain) with ZMIZ1 (via SP-RING-type domain); in the TGF-beta signaling pathway increases the activity of the SMAD3/SMAD4 transcriptional complex.
The MH1 domain is required for DNA binding.
The MH2 domain is required for both homomeric and heteromeric interactions and for transcriptional regulation. Sufficient for nuclear import.
Belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
References
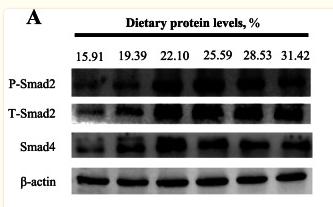
Application: WB Species: grass carp Sample: muscle
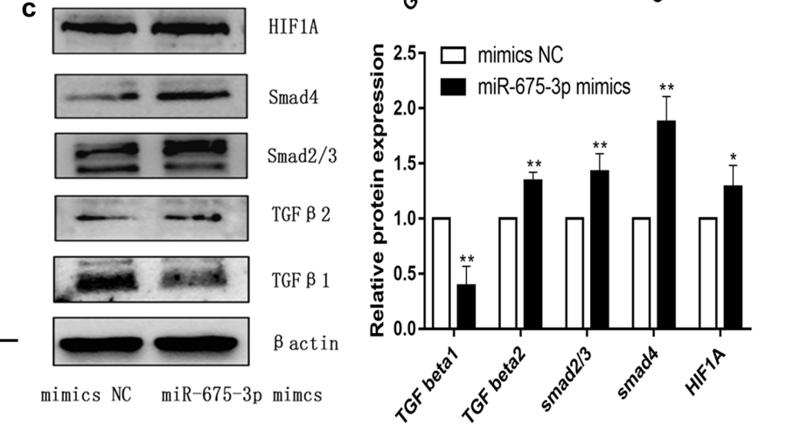
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: melanoma A375 cells
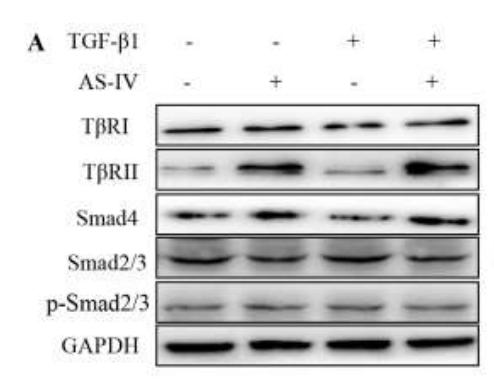
Application: WB Species: human Sample: SW962 cells
Application: WB Species: grass carp Sample: muscle
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.