Phospho-MST1(Thr183)/MST2(Thr180) Antibody - #AF2367
| Product: | Phospho-MST1(Thr183)/MST2(Thr180) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF2367 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-MST1(Thr183)/MST2(Thr180) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 59kDa; 56kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q13043 | Q13188 |
| RRID: | AB_2845381 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF2367, RRID:AB_2845381.
Fold/Unfold
Kinase responsive to stress; Krs2; Mammalian STE20 like protein kinase 1; Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 1; Mammalian sterile 20 like 1; MST-1; MST1; Serine/threonine kinase 4; Serine/threonine protein kinase Krs 2; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4; Serine/threonine-protein kinase Krs-2; STE20 like kinase MST1; STE20-like kinase MST1; STK4; STK4_HUMAN; TIIAC; YSK3; 0610042I06Rik; EC 2.7.11.1; FLJ90748; KB 1458E12.1; Kinase responsive to stress 1; KRS1; Mammalian STE20 like protein kinase 2; Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 2; Mammalian sterile 20-like 2; Mess1; MST; MST-2; MST2; Mst3; Serine/threonine kinase 3 (STE20 homolog, yeast); Serine/threonine kinase 3 (Ste20, yeast homolog); Serine/threonine kinase 3; Serine/threonine protein kinase 3; Serine/threonine protein kinase Krs1; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3; Serine/threonine-protein kinase Krs-1; STE20 like kinase MST2; STE20-like kinase MST2; Stk3; STK3_HUMAN; wu:fc19e11; zgc:55383;
Immunogens
Expressed in prostate cancer and levels increase from the normal to the malignant state (at protein level). Ubiquitously expressed.
Q13188 STK3_HUMAN:Expressed at high levels in adult kidney, skeletal and placenta tissues and at very low levels in adult heart, lung and brain tissues.
- Q13043 STK4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
METVQLRNPPRRQLKKLDEDSLTKQPEEVFDVLEKLGEGSYGSVYKAIHKETGQIVAIKQVPVESDLQEIIKEISIMQQCDSPHVVKYYGSYFKNTDLWIVMEYCGAGSVSDIIRLRNKTLTEDEIATILQSTLKGLEYLHFMRKIHRDIKAGNILLNTEGHAKLADFGVAGQLTDTMAKRNTVIGTPFWMAPEVIQEIGYNCVADIWSLGITAIEMAEGKPPYADIHPMRAIFMIPTNPPPTFRKPELWSDNFTDFVKQCLVKSPEQRATATQLLQHPFVRSAKGVSILRDLINEAMDVKLKRQESQQREVDQDDEENSEEDEMDSGTMVRAVGDEMGTVRVASTMTDGANTMIEHDDTLPSQLGTMVINAEDEEEEGTMKRRDETMQPAKPSFLEYFEQKEKENQINSFGKSVPGPLKNSSDWKIPQDGDYEFLKSWTVEDLQKRLLALDPMMEQEIEEIRQKYQSKRQPILDAIEAKKRRQQNF
- Q13188 STK3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEQPPAPKSKLKKLSEDSLTKQPEEVFDVLEKLGEGSYGSVFKAIHKESGQVVAIKQVPVESDLQEIIKEISIMQQCDSPYVVKYYGSYFKNTDLWIVMEYCGAGSVSDIIRLRNKTLIEDEIATILKSTLKGLEYLHFMRKIHRDIKAGNILLNTEGHAKLADFGVAGQLTDTMAKRNTVIGTPFWMAPEVIQEIGYNCVADIWSLGITSIEMAEGKPPYADIHPMRAIFMIPTNPPPTFRKPELWSDDFTDFVKKCLVKNPEQRATATQLLQHPFIKNAKPVSILRDLITEAMEIKAKRHEEQQRELEEEEENSDEDELDSHTMVKTSVESVGTMRATSTMSEGAQTMIEHNSTMLESDLGTMVINSEDEEEEDGTMKRNATSPQVQRPSFMDYFDKQDFKNKSHENCNQNMHEPFPMSKNVFPDNWKVPQDGDFDFLKNLSLEELQMRLKALDPMMEREIEELRQRYTAKRQPILDAMDAKKRRQQNF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q13043/Q13188 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K13 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S15 | Phosphorylation | P53350 (PLK1) | Uniprot |
| S18 | Phosphorylation | P53350 (PLK1) | Uniprot |
| K21 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K32 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K43 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K47 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K56 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y81 | Phosphorylation | P00519 (ABL1) | Uniprot |
| K116 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T117 | Phosphorylation | Q9Y243 (AKT3) , P31751 (AKT2) , P31749 (AKT1) | Uniprot |
| K128 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K148 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K161 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T174 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K177 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T180 | Phosphorylation | Q13188 (STK3) , Q7L7X3 (TAOK1) | Uniprot |
| T235 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T240 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K243 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K282 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K298 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S316 | Phosphorylation | P53350 (PLK1) | Uniprot |
| S323 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T325 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S333 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T336 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S369 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T378 | Phosphorylation | Q13188 (STK3) | Uniprot |
| T384 | Phosphorylation | P31749 (AKT1) | Uniprot |
| S385 | Phosphorylation | P06493 (CDK1) | Uniprot |
| S392 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y396 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S406 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C410 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K430 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S444 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K453 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| T3 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S21 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K24 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K35 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K35 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S40 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y41 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S43 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y45 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K46 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K50 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K59 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K59 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K72 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S82 | Phosphorylation | P45983 (MAPK8) | Uniprot |
| K119 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T120 | Phosphorylation | P31749 (AKT1) | Uniprot |
| S132 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K151 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K164 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T177 | Phosphorylation | Q13043 (STK4) | Uniprot |
| K180 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T183 | Phosphorylation | Q13043 (STK4) , P26927 (MST1) | Uniprot |
| T238 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T243 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K246 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K264 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S265 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K285 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S288 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S307 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S320 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S327 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T329 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T340 | Phosphorylation | O14757 (CHEK1) | Uniprot |
| T353 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T360 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T367 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T380 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T387 | Phosphorylation | Q9Y243 (AKT3) , Q13043 (STK4) , P31749 (AKT1) , P31751 (AKT2) | Uniprot |
| S394 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y398 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K404 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S410 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K413 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S414 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K420 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S422 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S423 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K426 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y433 | Phosphorylation | P00519 (ABL1) | Uniprot |
| K437 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S438 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T440 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K446 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
PTMs - Q13043/Q13188 As Enzyme
| Substrate | Site | Source |
|---|---|---|
| O95835 (LATS1) | S872 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | S909 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | T967 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | T1012 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | T1060 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | T1079 | Uniprot |
| P00519 (ABL1) | T735 | Uniprot |
| P17252 (PRKCA) | S226 | Uniprot |
| P17252 (PRKCA) | T228 | Uniprot |
| P18754 (RCC1) | S2 | Uniprot |
| P18754 (RCC1) | S11 | Uniprot |
| P46937 (YAP1) | S127 | Uniprot |
| P51955 (NEK2) | S356 | Uniprot |
| P51955 (NEK2) | S365 | Uniprot |
| P51955 (NEK2) | S406 | Uniprot |
| P51955 (NEK2) | S438 | Uniprot |
| Q13188 (STK3) | T180 | Uniprot |
| Q13188 (STK3) | T378 | Uniprot |
| Q7L9L4 (MOB1B) | T12 | Uniprot |
| Q7L9L4 (MOB1B) | T35 | Uniprot |
| Q7L9L4 (MOB1B) | T74 | Uniprot |
| Q9H492 (MAP1LC3A) | T50 | Uniprot |
| Q9H4B6 (SAV1) | T26 | Uniprot |
| Q9H4B6 (SAV1) | S27 | Uniprot |
| Q9H4B6 (SAV1) | S36 | Uniprot |
| Q9H4B6 (SAV1) | S269 | Uniprot |
| Q9H8S9 (MOB1A) | T12 | Uniprot |
| Q9H8S9 (MOB1A) | T35 | Uniprot |
| Q9H8S9 (MOB1A) | T74 | Uniprot |
| Q9NRM7 (LATS2) | S872 | Uniprot |
| Q9NRM7 (LATS2) | T1041 | Uniprot |
| Substrate | Site | Source |
|---|---|---|
| O43524 (FOXO3) | S209 | Uniprot |
| O43524 (FOXO3) | S215 | Uniprot |
| O43524 (FOXO3) | S231 | Uniprot |
| O43524 (FOXO3) | S232 | Uniprot |
| O43524 (FOXO3) | S243 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | S909 | Uniprot |
| O95835 (LATS1) | T1079 | Uniprot |
| P00519 (ABL1) | T735 | Uniprot |
| P19429 (TNNI3) | T31 | Uniprot |
| P19429 (TNNI3) | T51 | Uniprot |
| P19429 (TNNI3) | T129 | Uniprot |
| P19429 (TNNI3) | T143 | Uniprot |
| P33778 (HIST1H2BB) | S15 | Uniprot |
| Q06830 (PRDX1) | T18 | Uniprot |
| Q06830 (PRDX1) | T90 | Uniprot |
| Q06830 (PRDX1) | T183 | Uniprot |
| Q12778 (FOXO1) | S212 | Uniprot |
| Q13043-1 (STK4) | T177 | Uniprot |
| Q13043 (STK4) | T183 | Uniprot |
| Q13043-1 (STK4) | T187 | Uniprot |
| Q13043-1 (STK4) | S327 | Uniprot |
| Q13043 (STK4) | T387 | Uniprot |
| Q14457 (BECN1) | T108 | Uniprot |
| Q15208 (STK38) | T444 | Uniprot |
| Q7L9L4 (MOB1B) | T12 | Uniprot |
| Q7L9L4 (MOB1B) | T35 | Uniprot |
| Q96GD4 (AURKB) | T232 | Uniprot |
| Q9H492 (MAP1LC3A) | T50 | Uniprot |
| Q9H8S9 (MOB1A) | T12 | Uniprot |
| Q9H8S9 (MOB1A) | T35 | Uniprot |
| Q9NRM7 (LATS2) | S872 | Uniprot |
| Q9NRM7 (LATS2) | T1041 | Uniprot |
| Q9NS23-2 (RASSF1) | T202 | Uniprot |
| Q9NS23-2 (RASSF1) | S203 | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Stress-activated, pro-apoptotic kinase which, following caspase-cleavage, enters the nucleus and induces chromatin condensation followed by internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Key component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration. STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1 are required to repress proliferation of mature hepatocytes, to prevent activation of facultative adult liver stem cells (oval cells), and to inhibit tumor formation (By similarity). Phosphorylates 'Ser-14' of histone H2B (H2BS14ph) during apoptosis. Phosphorylates FOXO3 upon oxidative stress, which results in its nuclear translocation and cell death initiation. Phosphorylates MOBKL1A, MOBKL1B and RASSF2. Phosphorylates TNNI3 (cardiac Tn-I) and alters its binding affinity to TNNC1 (cardiac Tn-C) and TNNT2 (cardiac Tn-T). Phosphorylates FOXO1 on 'Ser-212' and regulates its activation and stimulates transcription of PMAIP1 in a FOXO1-dependent manner. Phosphorylates SIRT1 and inhibits SIRT1-mediated p53/TP53 deacetylation, thereby promoting p53/TP53 dependent transcription and apoptosis upon DNA damage. Acts as an inhibitor of PKB/AKT1. Phosphorylates AR on 'Ser-650' and suppresses its activity by intersecting with PKB/AKT1 signaling and antagonizing formation of AR-chromatin complexes.
Autophosphorylated on serine and threonine residues. Phosphorylation at Thr-387 by PKB/AKT1, leads to inhibition of its: kinase activity, nuclear translocation and autophosphorylation at Thr-183. It also diminishes its cleavage by caspases and its ability to phosphorylate FOXO3.
Proteolytically cleaved by caspase-3 during apoptosis at Asp-326 and Asp-349 resulting in a 37 kDa or a 39 kDa subunit respectively. The 39 kDa subunit is further cleaved into the 37 kDa form. Proteolytic cleavage results in kinase activation and nuclear translocation of the truncated form (MST1/N). It is less likely that cleavage at Asp-349 is a prerequisite for activation as this site is not conserved in the murine ortholog.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: The caspase-cleaved form cycles between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Expressed in prostate cancer and levels increase from the normal to the malignant state (at protein level). Ubiquitously expressed.
Homodimer; mediated via the coiled-coil region. Interacts with NORE1, which inhibits autoactivation. Interacts with and stabilizes SAV1. Interacts with RASSF1. Interacts with FOXO3. Interacts with RASSF2 (via SARAH domain). Interacts with AR, PKB/AKT1, TNNI3 and SIRT1. Interacts with DLG5 (via PDZ domain 3). Interacts with MARK3 in the presence of DLG5. Interacts with SCRIB in the presence of DLG5.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family. STE20 subfamily.
Stress-activated, pro-apoptotic kinase which, following caspase-cleavage, enters the nucleus and induces chromatin condensation followed by internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Key component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration. STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1 are required to repress proliferation of mature hepatocytes, to prevent activation of facultative adult liver stem cells (oval cells), and to inhibit tumor formation. Phosphorylates NKX2-1 (By similarity). Phosphorylates NEK2 and plays a role in centrosome disjunction by regulating the localization of NEK2 to centrosome, and its ability to phosphorylate CROCC and CEP250. In conjunction with SAV1, activates the transcriptional activity of ESR1 through the modulation of its phosphorylation. Positively regulates RAF1 activation via suppression of the inhibitory phosphorylation of RAF1 on 'Ser-259'. Phosphorylates MOBKL1A and RASSF2. Phosphorylates MOBKL1B on 'Thr-74'. Acts cooperatively with MOBKL1B to activate STK38.
Phosphorylation at Thr-117 and Thr-384 by PKB/AKT1, leads to inhibition of its: cleavage, kinase activity, autophosphorylation at Thr-180, binding to RASSF1 and nuclear translocation, and increase in its binding to RAF1.
Proteolytically cleaved by caspase-3 during apoptosis. Proteolytic cleavage results in kinase activation and nuclear translocation of the truncated form (MST1/N).
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: The caspase-cleaved form cycles between nucleus and cytoplasm (By similarity). Phosphorylation at Thr-117 leads to inhibition of nuclear translocation.
Expressed at high levels in adult kidney, skeletal and placenta tissues and at very low levels in adult heart, lung and brain tissues.
Homodimer; mediated via the coiled-coil region. Interacts with NORE1, which inhibits autoactivation (By similarity). Interacts with and stabilizes SAV1. Interacts with RAF1, which prevents dimerization and phosphorylation. Interacts with RASSF1. Interacts (via SARAH domain) with isoform 1 of NEK2. Interacts with ESR1 only in the presence of SAV1. Interacts with PKB/AKT1. Forms a tripartite complex with MOBKL1B and STK38. Interacts with RASSF2 (via SARAH domain). Interacts with DLG5 (via PDZ domain 3). Interacts with LATS1; this interaction is inhibited in the presence of DLG5. Interacts with MARK3 in the presence of DLG5.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family. STE20 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
References
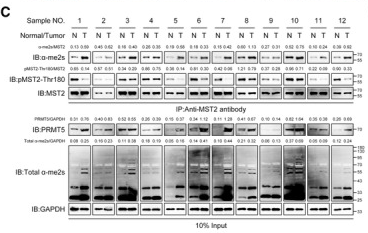
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: pancreatic cancer
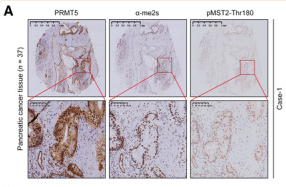
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample: pancreatic cancer
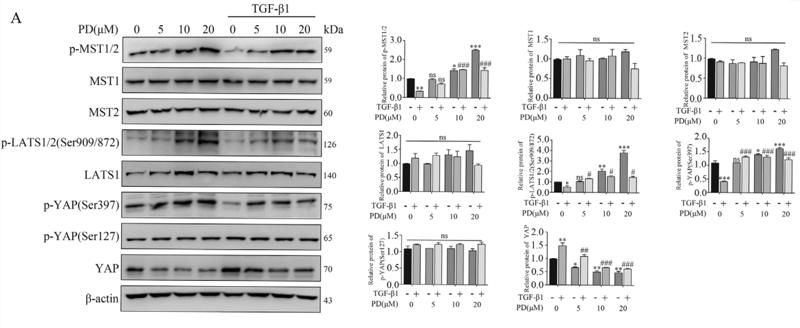
Application: WB Species: human Sample: LX-2 cells
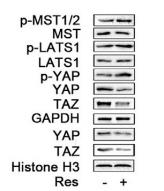
Application: WB Species: human Sample: FTC238 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.