Phospho-Smad2 (Ser465+Ser467) Antibody - #AF8314
| Product: | Phospho-Smad2 (Ser465+Ser467) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8314 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-Smad2 (Ser465+Ser467) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 58kDa; 52kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q15796 |
| RRID: | AB_2840376 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8314, RRID:AB_2840376.
Fold/Unfold
Drosophila, homolog of, MADR2; hMAD-2; HsMAD2; JV18; JV18-1; JV181; MAD; MAD homolog 2; MAD Related Protein 2; Mad-related protein 2; MADH2; MADR2; MGC22139; MGC34440; Mother against DPP homolog 2; Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2; Mothers against decapentaplegic, Drosophila, homolog of, 2; Mothers against DPP homolog 2; OTTHUMP00000163489; Sma and Mad related protein 2; Sma- and Mad-related protein 2 MAD; SMAD 2; SMAD family member 2; SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 2; SMAD2; SMAD2_HUMAN;
Immunogens
Expressed at high levels in skeletal muscle, endothelial cells, heart and placenta.
- Q15796 SMAD2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSSILPFTPPVVKRLLGWKKSAGGSGGAGGGEQNGQEEKWCEKAVKSLVKKLKKTGRLDELEKAITTQNCNTKCVTIPSTCSEIWGLSTPNTIDQWDTTGLYSFSEQTRSLDGRLQVSHRKGLPHVIYCRLWRWPDLHSHHELKAIENCEYAFNLKKDEVCVNPYHYQRVETPVLPPVLVPRHTEILTELPPLDDYTHSIPENTNFPAGIEPQSNYIPETPPPGYISEDGETSDQQLNQSMDTGSPAELSPTTLSPVNHSLDLQPVTYSEPAFWCSIAYYELNQRVGETFHASQPSLTVDGFTDPSNSERFCLGLLSNVNRNATVEMTRRHIGRGVRLYYIGGEVFAECLSDSAIFVQSPNCNQRYGWHPATVCKIPPGCNLKIFNNQEFAALLAQSVNQGFEAVYQLTRMCTIRMSFVKGWGAEYRRQTVTSTPCWIELHLNGPLQWLDKVLTQMGSPSVRCSSMS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q15796 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ubiquitination | Uniprot | ||
| S2 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S2 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T8 | Phosphorylation | P27361 (MAPK3) , P24941 (CDK2) | Uniprot |
| K13 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K19 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K20 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S21 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K39 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K46 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| S47 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K63 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y102 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S110 | Phosphorylation | Q9UQM7 (CAMK2A) , Q9H4A3 (WNK1) | Uniprot |
| S118 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K121 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y128 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K156 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K156 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K157 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y165 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T172 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T197 | Phosphorylation | P25098 (GRK2) | Uniprot |
| T220 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) , P27361 (MAPK3) | Uniprot |
| S240 | Phosphorylation | Q9UQM7 (CAMK2A) | Uniprot |
| S245 | Phosphorylation | Q14680 (MELK) , P28482 (MAPK1) , P27361 (MAPK3) | Uniprot |
| S250 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) , P27361 (MAPK3) | Uniprot |
| S255 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) , P27361 (MAPK3) | Uniprot |
| S260 | Phosphorylation | Q9UQM7 (CAMK2A) , Q9H4A3 (WNK1) | Uniprot |
| S317 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T324 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S417 | Phosphorylation | Q13177 (PAK2) | Uniprot |
| K420 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S458 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S460 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S464 | Phosphorylation | P36897 (TGFBR1) , O00238 (BMPR1B) | Uniprot |
| S465 | Phosphorylation | Q9H4A3 (WNK1) , P36897 (TGFBR1) , O00238 (BMPR1B) , O96013 (PAK4) , Q8NER5 (ACVR1C) | Uniprot |
| S467 | Phosphorylation | O00238 (BMPR1B) , P36897 (TGFBR1) , Q8NER5 (ACVR1C) | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD) that is an intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinases. Binds the TRE element in the promoter region of many genes that are regulated by TGF-beta and, on formation of the SMAD2/SMAD4 complex, activates transcription. May act as a tumor suppressor in colorectal carcinoma. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator.
Phosphorylated on one or several of Thr-220, Ser-245, Ser-250, and Ser-255. In response to TGF-beta, phosphorylated on Ser-465/467 by TGF-beta and activin type 1 receptor kinases. TGF-beta-induced Ser-465/467 phosphorylation declines progressively in a KMT5A-dependent manner. Able to interact with SMURF2 when phosphorylated on Ser-465/467, recruiting other proteins, such as SNON, for degradation. In response to decorin, the naturally occurring inhibitor of TGF-beta signaling, phosphorylated on Ser-240 by CaMK2. Phosphorylated by MAPK3 upon EGF stimulation; which increases transcriptional activity and stability, and is blocked by calmodulin. Phosphorylated by PDPK1.
In response to TGF-beta, ubiquitinated by NEDD4L; which promotes its degradation. Monoubiquitinated, leading to prevent DNA-binding (By similarity). Deubiquitination by USP15 alleviates inhibition and promotes activation of TGF-beta target genes. Ubiquitinated by RNF111, leading to its degradation: only SMAD2 proteins that are 'in use' are targeted by RNF111, RNF111 playing a key role in activating SMAD2 and regulating its turnover (By similarity).
Acetylated on Lys-19 by coactivators in response to TGF-beta signaling, which increases transcriptional activity. Isoform short: Acetylation increases DNA binding activity in vitro and enhances its association with target promoters in vivo. Acetylation in the nucleus by EP300 is enhanced by TGF-beta.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Cytoplasmic and nuclear in the absence of TGF-beta. On TGF-beta stimulation, migrates to the nucleus when complexed with SMAD4 (PubMed:9865696). On dephosphorylation by phosphatase PPM1A, released from the SMAD2/SMAD4 complex, and exported out of the nucleus by interaction with RANBP1 (PubMed:16751101, PubMed:19289081).
Expressed at high levels in skeletal muscle, endothelial cells, heart and placenta.
Monomer; the absence of TGF-beta. Heterodimer; in the presence of TGF-beta. Forms a heterodimer with co-SMAD, SMAD4, in the nucleus to form the transactivation complex SMAD2/SMAD4. Interacts with AIP1, HGS, PML and WWP1 (By similarity). Interacts with NEDD4L in response to TGF-beta (By similarity). Found in a complex with SMAD3 and TRIM33 upon addition of TGF-beta. Interacts with ACVR1B, SMAD3 and TRIM33. Interacts (via the MH2 domain) with ZFYVE9; may form trimers with the SMAD4 co-SMAD. Interacts with FOXH1, homeobox protein TGIF, PEBP2-alpha subunit, CREB-binding protein (CBP), EP300, SKI and SNW1. Interacts with SNON; when phosphorylated at Ser-465/467. Interacts with SKOR1 and SKOR2. Interacts with PRDM16. Interacts (via MH2 domain) with LEMD3. Interacts with RBPMS. Interacts with WWP1. Interacts (dephosphorylated form, via the MH1 and MH2 domains) with RANBP3 (via its C-terminal R domain); the interaction results in the export of dephosphorylated SMAD3 out of the nucleus and termination of the TGF-beta signaling. Interacts with PDPK1 (via PH domain). Interacts with DAB2; the interactions are enhanced upon TGF-beta stimulation. Interacts with USP15. Interacts with PPP5C. Interacts with ZNF580. Interacts with LDLRAD4 (via the SMAD interaction motif). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with PMEPA1 (via the SMAD interaction motif). Interacts with ZFHX3. Interacts with ZNF451. Identified in a complex that contains at least ZNF451, SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4. Interacts weakly with ZNF8 (By similarity). Interacts (when phosphorylated) with RNF111; RNF111 acts as an enhancer of the transcriptional responses by mediating ubiquitination and degradation of SMAD2 inhibitors (By similarity).
Belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
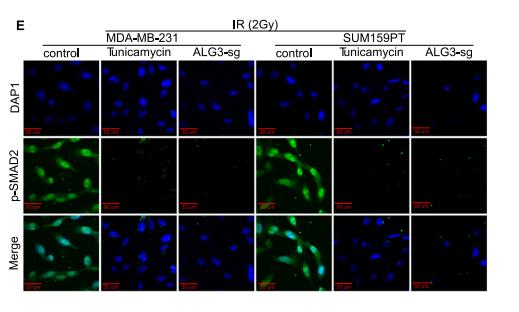
Application: IF/ICC Species: mouse Sample: ALG3-sg cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: CFs
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HepG2 cells
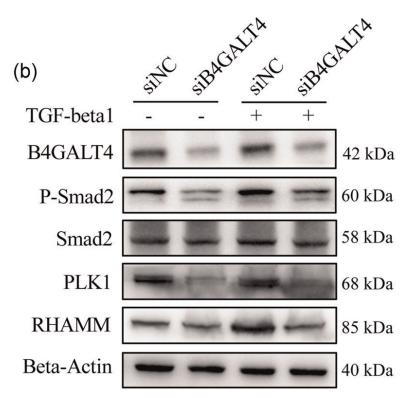
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: LX‐2 cells
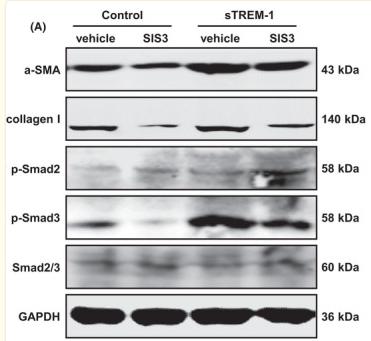
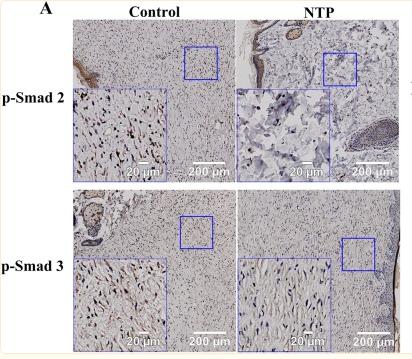
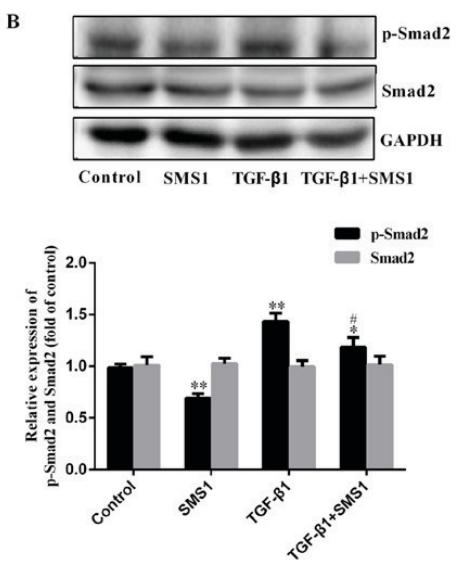
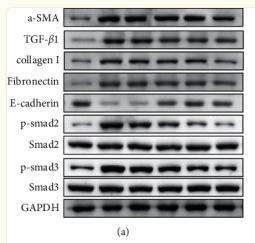
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: scar tissue
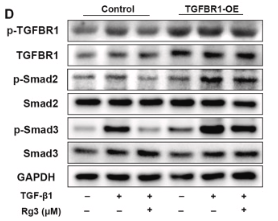
Application: WB Species: human Sample: MDA?MB?231 cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.